Highly Skilled Professional 70P&75P to Permanent Residency
 If I have more than 70 Points of Highly-Skilled Professional (HSP), can I apply for permanent residence for only 3 years stay in Japan?
If I have more than 70 Points of Highly-Skilled Professional (HSP), can I apply for permanent residence for only 3 years stay in Japan?
 If you have a Japanese degree, JLPT N1, sufficient salary, and 70 or more HSP points in the last 3 years, you can apply for PR now.
If you have a Japanese degree, JLPT N1, sufficient salary, and 70 or more HSP points in the last 3 years, you can apply for PR now.
Permanent Residency for HSP(70 points +)
Highly skilled People—those who score above 70 points on the Highly Skilled Professional (HSP) assessment—are now subject to relaxed residency requirements for permanent residency applications in Japan. Not only those residing under the Highly Skilled Professional visa, but also those currently on a Professor Visa, a WORK VISA (GIJYUTSU・JINBUNCHISHIKI・KOKUSAIGYOUMU VISA), or a Spouse Visa, may be eligible for these relaxed measures if they score over 70 points in the HSP assessment. It’s important to note that applicants do not need to currently hold a Highly Skilled Professional visa to qualify.
For those on a work visa, the requirement has typically been “a residency period of over 10 years, with at least 5 years spent working.” However, for individuals holding a Highly Skilled Professional visa (scoring above 70 points), as well as those scoring above 70 points in the HSP evaluation on other types of visas, the minimum residency period for permanent residency application is reduced to just 3 years.
Moreover, people scoring over 80 points may be eligible to apply for permanent residency in as short a period as one year.

Requirements for Permanent Residency(PR)
①Score of 70 or higher in the calculation at the time of application for PR
②Score of 70 or higher as calculated as of 3 years before you apply
70+HSP calculated when applying and 3 years prior to applying
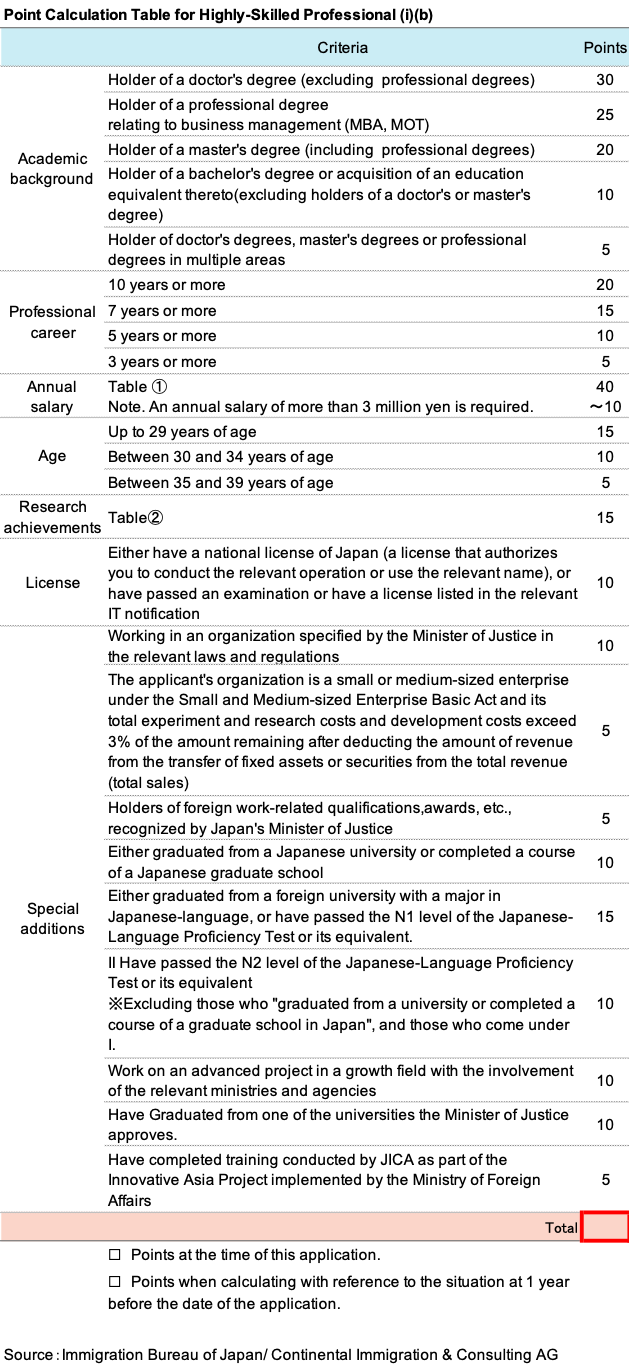
For HSP1a (Professor, Researcher), 1b (Company Employee, Engineer), and 1c ( Business Manager), points are assigned for degree, university of origin, professional experience, annual income, and Japanese proficiency.
You can apply for permanent residence if you meet at least 70 points in each of these categories when calculated at the time of application for permanent residence and three years prior to the application. The following is an example of the most common case of HSP1b (company employee, engineer, etc.).



Items to be scored to the HSP Point calculation
The main evaluation items for point calculation are (1) degree, university attended, (2) professional experience, (3) annual salary, (4) age, and (5) Japanese language ability. The higher the degree, the more points are given. The longer the work experience, the higher the annual income, and the younger the age, the more points will be given. In addition, points will be given for Japanese language proficiency if the applicant has JLPT N1.
In addition, graduates of universities with high ranking in GS,THE, researchers, approved IT qualification holders, and financial professionals, each may receive additional points.
Simply put, a Japanese university graduate with a JLPT N1, a master’s degree or higher, a graduate of a well-known university, and an IT technician are likely to score above 70 points on the HSP.
CASE STUDY
【CASE1】20s, Master (in Japan), 3 yeas business experience
In Highly Skilled Professional 1b, the distribution of points for education (maximum 30 points + 10 points from Japanese universities + 10 points from GS, THE High Ranking University), annual salary (maximum 40 points), and professional experience (maximum 20 points) will greatly affect the total score.
In general, 20s people have shorter professional experience and often do not have high annual incomes. Therefore, if applicants have a doctoral, master’s, or MBA degrees and the degrees are from Japanese universities or high ranking universities of QS or THE, they are more likely to meet the score criteria.If you have N1 of JLPT, you will receive additional points.

Of course, various cases can be assumed, but because of the significant impact of annual salary, sectors with high salary levels even in their 20s, such as IT and finance, are more likely to fall under the 70+ point scale. In particular, IT engineers will receive special points if they have certain IT qualifications.
【CASE2】Age:35-39, Bachelor(NOT in Japan), Salary 7 million JPY
This is the case for people in their late 30s. This group can expect to score more points in their professional careers after a long time since they graduated from university, and their salary level will be higher than those in their 20s. They also have a more diverse mix of higher degrees, JLPT proficiency, and various national certifications than 20s people.

※Learn more : HSP Points 80+
Requirement for Permanent Residency
Except HSP points
Foreign nationals with 70 or more Highly Skilled Professional points when calculated can apply for permanent residence with a minimum stay of three years. However, permanent residence requirements will be strictly examined. Now, let’s check the other criteria for permanent residence examination.
①Good conduct(means Compliance with Laws and Regulations)
②Sufficient income and assets
③Conformity with Japan’s national interests
④Appropriate guarantor
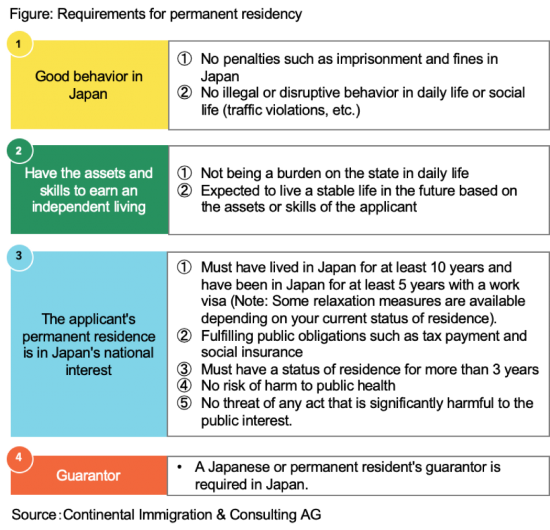
(1)Good conduct (Compliance with Laws and Regulations)
① No legal penalties have been imposed for violating the laws of Japan
The applicant must not have violated any Japanese laws and regulations and have not been sentenced to imprisonment or fined. However, in the case of imprisonment and KINKO, the applicant is not considered an ex-offender if 10 years have passed since his/her release from prison or 5 years have passed since the expiration of the probation period (SHIKKO YUYO), and in the case of fines, KORYU and TOGARYO, 5 years have passed. In addition, protective measures under the Juvenile Law must have been completed. These are including applicant’s family.

②No minor illegal acts or harassment to society
The requirement is that you do not repeatedly make minor violations of the law that do not constitute a legal penalty or inconvenience the community. Includes fines for traffic offenses.
Traffic offense
The penalty for traffic offenses is not a legal penalty, but if you repeatedly pay the penalty, you are repeatedly committing illegal activity. At present, it is difficult to estimate the number of traffic violations etc. in the examination process at least 5 times in the past 5 years and at least 4 times in the past 2 years. For example, it is not often memorized that a ticket was illegally locked due to parking prohibition, so you can get a driving record certificate at a police station and check it.
In the case of serious offenses such as unlicensed driving, drunk driving, and running away, it is necessary to wait five years after payment of fines is completed.

(2)Sufficient income and assets
The Immigration Bureau requires that “the applicant must not be a burden on the Japanese government and must have sufficient income and assets. Not being a burden on the government means not receiving public assistance, pension or tax exemptions.
In addition, the minimum income requirement is at least 3 million yen for the past 1 to 3 consecutive years. However, depending on the number of dependents, a larger income amount is required. Generally, about ¥800,000 per dependent is said to be added.
In other words, a person who supports a wife, two children, and two parents would have an annual income of about 3,000,000 yen + 800,000 yen x 5 persons = 7,000,000 JPY.
When you change jobs
Highly Skilled Professional visa holders must apply for permission to change their status of residence each time they change jobs. The background of HSP points changes depending on the job change. If an applicant repeatedly changes jobs, his/her permanent residence may be denied due to a lack of stability in employment. Therefore, it is desirable for the applicant to have been working for at least one year after changing jobs.
(3)Conformity with Japan’s national interests
It is important that the permanent residence of the applicant is in the interest of Japan. Specifically, there are 5 points.
①Must have HSP points of 70 or more and have been residing in Japan for more than 3 year continuously. Or Must have HSP points of 80 or more and have been residing in Japan for more than one year continuously.
②Public obligations such as tax payment and social insurance
Taxes such as income tax, resident tax, and corporate tax, as well as pensions such as employee pensions and national pensions must be properly paid and not payable. In addition, they are not asking whether you paid the final payment, but rather whether you are paying on time. If you have not paid taxes or pensions, or you have paid but have not paid by the due date, you will not be allowed.
If you do not pay within the payment deadline
If you fail to pay on time, you must have a record of legal payment for the next two years after you pay the outstanding amount. You will also need to explain to the immigration authorities why you failed to pay on time and how to prevent a recurrence. Recurrence prevention measures include the use of bank direct debit or credit card payments.
To begin with, if you are not a member of the National Pension System, you must join the National Pension System, pay your outstanding payments and keep a record of your membership for two years.
Number of legally dependent families
In order to pay taxes, you must be properly dependent on tax law. If a relative who is not originally permitted under tax law is being supported for the purpose of reducing tax payments, permanent residence is not permitted because he / she does not fulfill the appropriate tax obligations (= tax evasion).
③3 or 5 years Visa are Required
Highly-Skilled Professional (HSP) residency status is granted for five years. However, if you have a status which is not HSP, your current status of residence must be for three years or more. If your current status is less than three years old, you must change your status to HSP before you can apply for permanent residence.
④There is no risk of harm from a public health perspective.
Specifically, you must not be addicted to drugs, marijuana, or stimulants, and you must not have contracted any infectious diseases such as Ebola hemorrhagic fever or plague.
⑤There is no risk of committing an act that is materially harmful to the public interest.
The content here is similar to the requirements for conduct in (1).
(4)You need a GUARANTOR
You need a guarantor (身元保証人) when you apply your Permanent Residence for the Japanese Immigration Bureau. Only Japanese national people or “Permanent Resident Status in Japan” are available. Only those with a stable income and who have paid their tax obligations can be a guarantor for permanent residence applications. In other words, a person who is unemployed or has not legally declared personal income is ineligible.
[Responsibilities of guarantor] The guarantor’s guarantee consists of three parts: 1) payment for accommodation expenses, 2) payment for return expenses, and 3) legal compliance of the applicant.The guarantor under the immigration law is morally responsible and has no legal responsibility.In other words, there is no legal obligation to pay the applicant’s stay and return expenses, and he is not responsible for overseeing any violations of the applicant. However, a guarantor that has failed to fulfill its moral obligations to the applicant will no longer be able to become an guarantor for another permanent resident application.If no guarantor can be obtained, some companies may refer you to an guarantor. However, the Immigration Bureau dislikes anyone who is unrelated to the applicant from becoming an identity guarantor, which can be negative for permanent residence permits.
(For your reference:How to asking for a guarantor for a permanent residence application)
Examination period
The standard examination period for permanent residence applications at the Immigration Bureau is 4 months, but at the time of this writing (November 2023), it actually takes from 8 to 10 months. As with other visas, it varies depending on the applicant’s situation, the time of application, and the immigration office where the application was filed. In line with stricter screening procedures, the approval rate for permanent residence examinations has also been declining.
FYI:How to speed up PR examination period
Our Insight
Applicants with HSP points of 70 or more should be actively considered for permanent residence, as the length of stay is greatly eased. However, the permanent residence examination process is rigorous and the examination period is long, so adequate preparation is required. If you have any questions, please do not hesitate to contact our Continental specialists.
Fee for HSP-PR:170,000 (Including tax 187,000 JPY)
Obtaining the Japanese government Documents and new residence card on behalf of you :+50,000 JPY including document’s costs
Professional
 Masakazu Murai
Masakazu Murai
Immigration consultant, Financial advisor
18 years experience in Investment Banking at Mitsubishi UFJ Morgan Stanley. He had provided financial advisory more than 500 entrepreneurs and senior management.
During his tenure, he worked as an employee union executive committee member in promoting diversity, including the active participation of foreigners and women in the workplace, and engaged in activities to improve the working environment. He specializes in consulting and financial consulting on the status of residence for foreigners.
Gyoseishoshi Immigration Lawyer
CMA(Japanese financial analyst license)
CFP (Certified Financial Planner)
Master of Business Administration in Entrepreneurship (Hosei Business School)











